Venezuela Impacts G20 And More; Resolution Should Be A Priority
Lack Of Triangular Trust Is Profound
“Hard Choices”
Closing Borders? The Syria Model
Is “Economic Waterboarding” Necessary For 32 Million People?
Five Members Of The G20 Are Primary For A Resolution
Seven Global Impacts Because Of Venezuela’s Instability
Cuba Has A Role
The Five-Step Roadmap
Why are thirty-two million residents of Venezuela victimized by “economic waterboarding”- not once, not twice, but every day- and every hour of every day?
First, because of decisions by the government of Venezuela; that’s an inescapable conclusion. Second, because none of the consequential actors agree as to the definition of the problem. Third, because none of those actors will make hard choices- which may require (perhaps temporarily) separating self-interest from the interests of the dispossessed.
The issue is not uniquely about crossing lines, red or any other color, it’s about removing boundaries which are effectually barriers to communication to solve the problem.
Is Venezuela solvable? Yes. The equation required is neither linear nor one dimensional. The solution requires decisions that optically are unpleasant. Absent correction, what represents approximately 10% of the population of the United States will remain unwelcomed, unresponsive, unproductive and increasingly simultaneously angry and dispirited- 1,377 miles south east of Key West, Florida. All the while atop the world’s largest proven oil reserves (Iran ranks third/fourth).
For a resident of Venezuela, the debate among governments as to who to hold responsible, how to hold them responsible and where to hold them responsible is of far less importance than finding water, food, medication and employment. They want a solution rather than awaiting results from a caloric-depleting gaming theory played-out by elected and appointed officials in capitals around the world- none of whom are lacking in food, clothing or paycheck.
For the outlying governments- near and abroad, they await a population that erupts to topple the Maduro Administration; an energy-depleted population without cohesive leadership. The hoped-for result takes time- with the outlying governments patient while the population suffers-along-to-victory.
The lack of a sustainable trilateral trust among the United States, Venezuela and the Republic of Cuba remains profound and unless addressed will serve as the primary impediment to resolving the respective bilateral issues and ultimately the trilateral issues.
The commercial, economic and political issues enveloping Venezuela are a global contagion impacting each member (and beyond) of the G20, G7, OAS and UN.
Lack of a resolution for Venezuela continues to impact globally the a) price of crude oil b) price of natural gas c) prices of distillates (fuels and fuel oils) d) range of interest rates governments must pay, companies must pay and consumers must pay e) cost of bonds f) value of stock markets and g) decisions by country central banks.
Why does Venezuela matter? Venezuela has the largest proven oil reserves in the world, the eighth-largest natural gas reserves in the world and has been the twenty-seventh (27th) largest gold producer in the world. Venezuela’s population of 32 million ranks 44th among 233 countries. As the crow flies, the capital Caracas is 2,060 miles south from Washington DC. And, the connectively of Venezuela and Iran, with respect to how issues relating to each impact global energy markets and global political discourse, is another reason that a resolution for Venezuela is important.
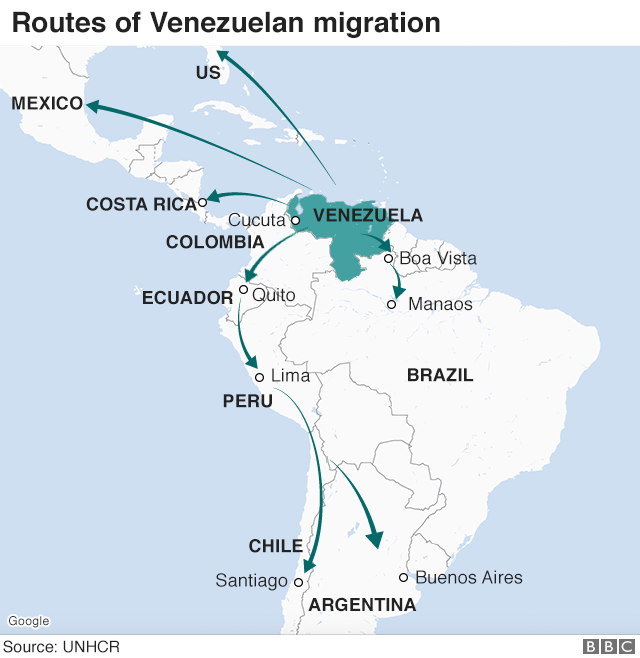
G20 members- Brazil (which shares a 1,367 mile border with Venezuela), China, Russia, Turkey and United States have defining roles in determining how costly is a resolution for each of the 32 million citizens of Venezuela- approximately four million of whom have departed the country during the last four (4) years with approximately one (1) million having departed in the last five (5) months.
To date, the imperfect defacto consensus for Venezuela by Brazil, Venezuela, China, Russia, Turkey and the United States is 1) something needs to happen 2) absence of a resolution remains a preferred landscape; and the cost of repair and replace and hardship inflicted upon the 32 million citizens of Venezuela remains within acceptable political parameters 3) the solution must birth itself from within Venezuela, although the definition of “birth itself” is not shared by the five parties 4) there is no trust among the five 5) none of the five will publicly say that they’ve done anything wrong 6) no agreement as to the definition of the problem and what, if anything, needs to be done and 7) some members of the five take pride in advancing and/or sustaining the status quo precisely because of the indigestion and distraction and internal recrimination brought to the overseas doorstep of the United States. Until some or all of the calculus changes, Venezuela remains a global contagion.
Predictive modeling analysis to determine at least two outcomes is easily calculable and subject to calibration: None of the five primary actors will permit Venezuela to implode or explode. The five primary actors are (agnostically) permissive of permitting extreme pain- a multiple-times-per-day economic waterboarding for 32 million citizens- without consistent messaging as to what the population need collectively to do for the pain to end.
It’s about surrendering. The question is who surrenders to whom? The government to the governed or the governed to the government?
Some context: The United Nations reported that of Syria’s 21 million pre-2011 population, today 13.5 million require humanitarian assistance, more than 6 million are “internally displaced” (a delicate way to convey their homes are uninhabitable; not visiting relatives or on vacation), and more than 6 million have left the country. Turkey (population 82 million) is hosting a reported 3.6 million; Lebanon (population 6 million) is hosting 1.5 million, and Jordan (population 10 million) is hosting 1.4 million. The cost to reconstitute what was in 2011? Perhaps, US$50 billion to US$100 billion- another commercial opportunity.
There were border-closing propositions debated from 2011 through 2013 where the Obama Administration would have led a coalition including Jordan, Iraq, Israel, Lebanon and Turkey to close their respective borders soon after the initial violence in Syria. Had those propositions been adopted, the multi-year, multi-billion-dollar tragedy that has infiltrated and disrupted the European Continent may have been mitigated.
If Jordan, Iraq, Lebanon and Turkey had closed their borders in 2011 and governments (particularly the United States) had not closed their embassies and those of Syria in other countries, the Assad Administration would have been forced to embrace a far less catastrophic strategy due to a lack of commercial, economic and political oxygen- and a robust diplomatic presence throughout the country. What’s happened in Syria is much easier to accomplish when nearing one-in-three citizens have departed the country.
The United Nations reported that since 2014 approximately 4 million have departed Venezuela. If Aruba, Brazil, Colombia Curacao, Guyana, and Trinidad and Tobago had closed their borders in 2018 or 2019, the Maduro Administration, lacking commercial, economic and political value from purging the unwanted, would have chosen a less catastrophic strategy due to a lack of commercial, economic and political oxygen.
For those countries whose borders are continuous and connected to Venezuela- Brazil, Colombia and Guyana, stability is far more paramount than is the immediate composition, the character of leadership in Caracas. Each remain impacted by an unstable Venezuela due to impact upon energy deliveries, immigration, and political relationships.
Colombia (population 49.85 million), sharing a 1,378 mile border with Venezuela, has been most impacted by a reported more than 1.5 million citizens of Venezuela arriving to during the last several years resulting in an increase in unemployment, depression of wages, stresses upon educational systems, impact upon social services, and an increase in crime particularly in the capital, Bogota (population 8 million). Colombia’s borders also include Panama, Ecuador, Peru and Brazil, so the country is a point of transit for refugees seeking to travel to Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina and these countries have implemented immigration policies to curb arrivals due to the same issues impacting Colombia. According to the United States Department of State, Peru (population approximately 32.17 million) is hosting approximately 800,000 migrants/refugees from Venezuela and Ecuador (population approximately 16.65 million) is hosting approximately 260,000 migrants/refugees from Venezuela.
Though painful for all parties, Brazil, Colombia and Guyana can still close their borders with Venezuela. The result would expectantly lessen the duration of the Maduro Administration- but, at what societal and reputational cost? With border closures, the problems within Venezuela would then remain within the borders of Venezuela- requiring the Maduro Administration to adopt commercial, economic and political changes or preside over a chain reaction of implosions and explosions certain to lead to unpleasant final chapter.
The closure of borders is painful for those who are trapped, but shorter-term pain is probably preferred to longer-term generational mismanagement in providing opportunities to a population.
Economic waterboarding has become an ever-more frequent instrument for those in government to remain in government and for those out of government to return to government and for those seeking to be the government: Afghanistan, Democratic Republic of Congo, Iraq, Israel/Palestine, Libya, Nigeria, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Syria, Yemen and Zimbabwe come to mind as reported examples.
Another instrument of population pain is the concept of Apartheid, having its roots in segregation and subjugation by race (white on black), but has from end of the 20th century and thus far through the 21st century carried-forth defined not only by race (which has transformed in some instances to black on black particularly on the continent of Africa), but to ethnicity, political perspective, party affiliation, and religious testament. Components of the 21st century apartheid appear in Venezuela. Traditionally, the role of global balancer would be the purview of the United States; that opportunity does not seem to be currently viable.
The problems inflicting Venezuela are self-inflicted due to the creation and implementation during more than twenty (20) years of policies, regulations and statutes that continue to impede export revenues, import revenues, debt servicing, and manufacturing/assembly productivity and efficiency. The decisions of third-parties have exacerbated the self-inflicted issues, but are not their cause.
For political leadership in Venezuela to prevail, primary focus need be upon transparency in the decision-making process, consistency in the decision-making process, and continuity in the decision-making process. With those three imperatives, Venezuela and other countries may model outcomes so that impact is both predictable and manageable.
The known is whatever the solution for Venezuela, the fulcrum component requires global stable pricing for crude oil so that the government of Venezuela and those who finance it (through direct/indirect lending and bond purchases) and those who manage it may project revenues and expenses.
Before Venezuela has the means to again redevelop its manufacturing and assembly infrastructure to support the aspirations of its 32 million citizens, its companies (domestic and subsidiaries of foreign companies) require pricing for its current primary export to be stable.
This means the United States and the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) need to cooperate.
One OPEC member is a member of the G20- Saudi Arabia; two OPEC Observers are members of the G20- Mexico and Russia.
Can, however, the United States, OPEC, OPEC Observers, and the countries who import oil through the complexities of the global marketplace, denominated in United States Dollars, create global stability where sources of energy and uses of energy continue to change whether a construct of pricing, environmental focus or both? The cooperative baseline will likely remain imperfect.
And For Cuba?
A resolution for Venezuela also dramatically impacts the Republic of Cuba- requiring the [Miguel] Diaz-Canel Administration to continue to accept, adapt, endure and maintain ongoing structural changes to the economic fabric and social fabric of the 800-mile archipelago for its 11.4 million citizens.
The most consequential challenge for the government of the Republic of Cuba is how to pivot from a commercial, economic and political landscape which has existed due to non-market-based benefits provided by third-parties to a landscape which the public sector and private sector function on the basis of market-based relationships with those it exports to, imports from, and provides services. Once achieved, the Republic of Cuba will have created an environment whereby it will have better control over the domestic direct and indirect impact of decisions by third-parties.
Prosperity in the Republic of Cuba has not been prevented, but has been impacted because of laws, regulations and policies of the United States. Prosperity has not revisited the Republic of Cuba primarily because the government of the Republic of Cuba remains fearful of the impact of prosperity upon the population. There is a fear of the “lottery curse” where those who have not had money suddenly have money and they mismanage it and, in some instances, it corrupts their soul.
First Published 30 March 2019
The Unresolved Commercial, Economic And Political Issues In Venezuela Remain A Bilateral And Multilateral Contagion
https://www.cubatrade.org/blog/2019/3/30/the-unresolved-commercial-economic-and-political-issues-in-venezuela-remain-a-bilateral-and-multilateral-contagion
Until there is a resolution, or the perception of a resolution to Venezuela amongst impacted constituencies, challenging will be resolve by the Trump Administration to engage the Republic of Cuba in direct bilateral negotiations about the certified claims or any other issue of substance.
There are decisions which could be implemented in Venezuela and in the Republic of Cuba that might prompt a shift in the political compass (and calculus) of the Trump Administration from directionally limited to normal activity. For that to happen, the Trump Administration needs to be succinct in the logic and practicality of its strategy and its messaging.
The Trump Administration must provide assurances to Russia and China that monies owed to them by Venezuela will be repaid and that the Trump Administration will not seek to prohibit or deter companies from Russia and China from bidding on, implementing, and receiving payment from contracts in the future.
First, H.E. Juan Guaido, President of the National Assembly of Venezuela and self-declared Interim President of Venezuela, should be unequivocal in stating he will not become a presidential candidate when the next election is scheduled. By confirming that his role is solely guiding Venezuela to its next presidential election, he would assist, but not eliminate, perceptions that he is too influenced by and beholden to interests of the United States. His not seeking higher office removes an impediment to resolving the problems of Venezuela.
Interim-President Guaido has limited time within which to demonstrate a landscape of control of the government of Venezuela- especially relating to the provision of services and particularly with respect to the distribution of substantial quantities of United States Dollars and other currencies located outside of Venezuela which the Trump Administration and other governments have sequestered for his control and then use on behalf of the citizens of Venezuela. There may be a moment where citizens of Venezuela, despite support for Interim-President Guaido, decide that too many of their county’s financial resources are inaccessible unless they support President Nicolas Maduro; and the international community generally has limited patience in maintaining potentially billions of United States dollars and other currencies in perpetuity for a Maduro-less or Maduro-light government of Venezuela.
Second, the Trump Administration has increased its usage of the phrasing “recognizing the realities on the ground” to discuss territorial issues. The reality on the ground in Venezuela is those serving in the armed forces of Venezuela will determine whether President Maduro departs, when he departs and how he departs. Unless there is an amnesty which includes departure from the country, if desired, and a guarantee that the United States and other countries will not pursue individuals for additional criminal or civil actions, challenging will be creating an atmosphere where members of the armed forces will support meaningful- and permanent change in Venezuela.
Third, President Maduro, should he decide to resign and remain in Venezuela or depart for another country, would require assurances that he and his family would not be pursued for criminal and civil charges. Perhaps, an unsettling and unappetizing possibility, but lacking such “not-go-to-jail cards and get-of-of-jail cards” the process of crisis- and the pain inflicted upon the citizens of Venezuela will continue- as will a question for those opposing President Maduro: What is most important- President Maduro becoming Mr. Maduro or holding President Maduro accountable when he becomes Mr. Maduro? There may not be a reasonable option to pursue both- there might be a forced choice. Is the goal solving the problem or maintaining the problem?
Fourth, if President Maduro departs Venezuela and the Republic of Cuba agrees to provide him with temporary or permanent housing, what should be the conditions? Other countries who might host President Maduro include Russia, Turkey or one of the other thirteen members of the Vienna, Austria-based Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
The Republic of Cuba would want guarantees from the United States, Organization of American States (OAS), European Union (EU), United Nations (UN) and International Criminal Court (ICC) among others that Mr. Maduro would not be sought for extradition and the Republic of Cuba would not be penalized for providing housing to Mr. Maduro.
The United States would need to choose- the Trump Administration has defined President Maduro and what has happened within Venezuela as a [mostly] creation of the Republic of Cuba and has stated that if the Republic of Cuba withdrew its support (military and intelligence) for President Maduro, the problems of Venezuela would become those for Mr. Guaido (until a new president is elected) and supporters to repair.
Political realities are often not binary and are multi-dimensional and lacking zero-sum definitions. The Trump Administration will likely not inhabit the Venezuela it projects to seek in the short-term to medium-term unless there is an agreement with the Republic of Cuba- who will not agree to be blamed by the Trump Administration for what is happening in Venezuela while simultaneously being blamed if it takes a meaningful decision to change the equation to what is sought by the Trump Administration by providing safe harbor to Mr. Maduro. Such self-imposed constraints on the Trump Administration would be challenging and equally so for members of the United States Congress.
Fifth, if the Republic of Cuba were to agree to provide housing for Mr. Maduro, it would expectantly seek from the Trump Administration an agreement to reverse some decisions it has already taken or not implement what it has yet to do; perhaps including reinstatement to the OAS and lessening some international transaction restrictions.
There is also logic for the Republic of Cuba to seek nothing from the Trump Administration and extract global goodwill for solving a problem which, by doing so, will result in economic pain for the Republic of Cuba. The Republic of Cuba’s reliance on Venezuela has continued to decrease during the last four years; so, while painful, the Republic of Cuba could manage an elimination of its preferential commercial agreements. If the Trump Administration were to then implement additional measures, they would be perceived by other countries as punitive- and the Republic of Cuba would gain leverage in the global marketplace- and in some constituencies throughout the United States.
The primary question for the Trump Administration: President Maduro is willing to let his people suffer; is the Trump Administration willing to let his people suffer? President Maduro has now survived past the presented expectations of the Trump Administration, so the distance between the Trump Administration obtaining everything that it wants and what is likely available continues to increase- that’s a problem for the Trump Administration.
The likely predicted outcome for Venezuela will neither have a winner or a looser. With President Maduro’s absence, all stakeholders will continue to endure pain while gaining or regaining what they want.
G7, G20, OAS, EU, OPEC Membership
G7: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, United Kingdom, and United States.
G20: Argentina, Brazil, China, Germany, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Russia, Turkey, United States, Australia, Canada, France, India, Italy, Mexico, Republic of South Africa, Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom, and Brussels, Belgium-based European Union (EU).
OAS: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Barbados, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, The Bahamas, Trinidad and Tobago, United States, Uruguay and Venezuela.
EU: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom.
OPEC: Algeria, Angola, Congo, Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Venezuela. OPEC Observers: Egypt, Mexico, Norway, Oman and Russia among other countries.
LINK To Complete Analysis In PDF Format