Six Months Since Libertad Act Lawsuits Permitted For Cuba. Has It Worked? We Don’t Know And May Never Know… That’s A Problem.
/If A Settlement Is Secret, Then Where Is The Deterrent?
Taxpayers Paid For It; Should Benefit From Knowing How It Is Used
All Settlements Using Title III Of The Libertad Act Should Be Public
Courts Are Public Entities- Any Decision/Settlement Should Be Public
The United States Department Of State Should Publish All Title IV Decisions
Some May Never See The Accountability They Seek
A Twenty-Three-Year-Old Volcano Has Come To Life- Everyone Needs To See The Lava
In 1996, the United States enacted a law specifically designed to deter the use of expropriated assets. A primary goal of the law was to publicly shame “traffickers” to cease activity in the Republic of Cuba- and do so in a high-wattage manner whereby others would be deterred from the same activity. The courts would serve as spotlights.
The Cuban Liberty and Democratic Solidarity Act of 1996 (known as “Libertad Act”) has been operational for more than six months; if all the court decisions, court judgements, settlements and out-of-court agreements are not fully disclosed in a timely manner, how will any taxpayer-funded deterrent be measurable?
The Libertad Act languished for twenty-three (23) years through three presidencies and half of a fourth presidency. A dormant volcano. When it spewed, it would cascade not lava, but notices, summonses, subpoenas, motions and appeals.
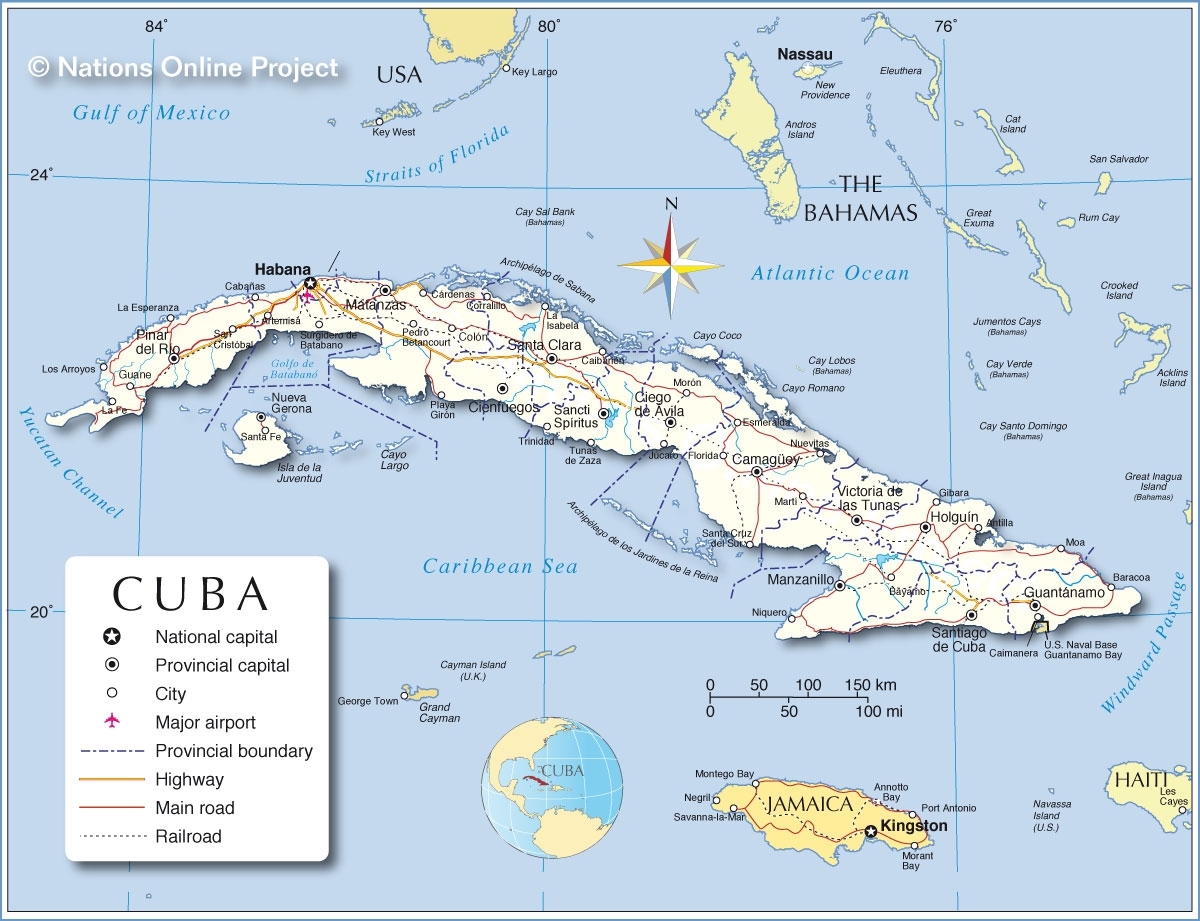
During the last 187-days, in four states a total of twenty (20) lawsuits have been filed by seventy-two (72) plaintiffs using Title III of the Libertad Act against sixty-seven (67) defendants. At least eighty-eight (88) attorneys from twenty-five (25) law firms are involved with the lawsuits presenting plaintiffs or defendants.
STATISTICS: Twenty (20) lawsuits filed; Court Filing Fees US$130,960.00; Twenty-Five (25) Law Firms; Eighty-Eight (88) Attorneys; US$1.1+ Million In Law Firm Billable Hours; One Hundred-And-Three (103) companies/individuals, excluding attorneys, are lawsuit parties; Seventy-Two (72) plaintiffs; Four (4) Class Action status requests; Sixty-seven (67) defendants; Five (5) companies notified as will be added as defendants unless prompt settlement. Lawsuits have been filed in the United States District Courts in Southern Florida (16), Washington DC (1), Washington State (1), Nevada (1) and Delaware (1). LINK To Complete Statistics Report
Law firms retained by plaintiffs/defendants: Akerman; Arent Fox; Baker & McKenzie; Boies Schiller Flexner; Coffey Burlington; Colson Hicks Eidson; Cueto Law Group; Ewusiak Law; Hogan Lovells; Holland & Knight; Jones Walker; Kozyak Tropin & Throckmorton; Law Offices Of Paul Sack; Manuel Vazquez PA; Margol & Margol; Mayer Brown; Pacifica Law Group; Rabinowitz, Boudin, Standard, Krinsky & Lieberman; Reed Smith; Reid Collins & Tsai; Rice Reuther Sullivan & Carroll; Rivero Mestre; Rosenthal, Monhait & Goddess; Steptoe & Johnson; Venable.
Title III authorizes lawsuits in United States District Courts against companies and individuals who are using a certified claim or non-certified claim where the owner of the certified claim or non-certified claim has not received compensation from the Republic of Cuba or from a third-party who is using (“trafficking”) the asset.
Given the immense domestic and international implications for decisions arising from the lawsuits, essential that all decisions be in the public domain.
This exposure is especially significant with respect to any “private settlements” among plaintiffs and defendants. The Libertad Act authorizes private settlements- a trafficker and owner of the expropriated asset can agree on compensation, but there is nothing in the Libertad Act compelling disclosure of any compensation.
Title IV of the Libertad Act restricts entry into the United States by individuals who have connectivity to unresolved certified claims or non-certified claims. One Canada-based company is currently known as subject to this provision based upon a certified claim.
The United States Department of State has refused to provide any information relating to the use of Title IV- not the number of letters sent, not the identity of the recipients, not whether any recipient has ceased “trafficking” as a result of receiving a letter.
There is value to current plaintiffs and defendants and to potential plaintiffs and defendants from having data from which they weigh the value of their lawsuit, the value of filing a lawsuit, and the value of seeking a Title IV letter.
From a United States-based law firm: “It’s a very odd and recent idea that settlements should be allowed to be secret. Without a court case, sure, people can settle their affairs with each other privately on any terms they like.
But once someone invokes a law that claims a public policy purpose, like the Libertad Act, then the citizens of this country ought to know exactly how that law is working in practice. Is it achieving its policy goals, or is just a means for Cuban Americans to extort tolls from businesses trading with and investing in Cuba? Think for example about American Airlines being sued for transporting passengers to and from Cuba under various federal licenses and route allocations. Clearly the United States government not only approved but encouraged the company to provide that service.
So, should that case be settled, doesn’t the public have a right to know what a litigant got from deploying a federal law against that United States company?
Another thing, the filing fee in a federal case doesn’t even cover the wages of the janitor who cleans the courtrooms. Taxpayers foot the bill for judges’ salaries and pensions, and law clerks and administrative staffs’ wages, the costs of bailiffs, the cost of court houses and their maintenance, and on and on. Why should someone be free to use that infrastructure to procure money from another private party without taxpayers knowing how much they actually received by using a public law and its enforcement mechanism, the federal court system?”
From the Chicago, Illinois-based American Bar Association (ABA) on United States Federal Courts Funding:
Libertad Act
The Trump Administration has made operational Title III and further implemented Title IV of the Cuban Liberty and Democratic Solidarity Act of 1996 (known as “Libertad Act”).
Title III authorizes lawsuits in United States District Courts against companies and individuals who are using a certified claim or non-certified claim where the owner of the certified claim or non-certified claim has not received compensation from the Republic of Cuba or from a third-party who is using (“trafficking”) the asset.
Title IV restricts entry into the United States by individuals who have connectivity to unresolved certified claims or non-certified claims. One Canada-based company is currently subject to this provision based upon a certified claim.
Suspension History
Title III was suspended every six months since the Libertad Act was enacted in 1996- by President William J. Clinton, President George W. Bush, President Barack H. Obama and President Donald J. Trump.
On 16 January 2019, The Honorable Mike Pompeo, United States Secretary of State, reported a suspension for forty-five (45) days.
On 4 March 2019, Secretary Pompeo reported a suspension for thirty (30) days.
On 3 April 2019, Secretary Pompeo reported a further suspension for fourteen (14) days through 1 May 2019.
On 17 April 2019, the Trump Administration reported that it would no longer suspend Title III.
On 2 May 2019 certified claimants and non-certified claimants were permitted to file lawsuits in United States courts.
Certified Claims Background
There are 8,821 claims of which 5,913 awards valued at US$1,902,202,284.95 were certified by the USFCSC and have not been resolved for nearing sixty years (some assets were officially confiscated in the 1960’s, some in the 1970’s and some in the 1990’s. The USFCSC permitted simple interest (not compound interest) of 6% per annum (approximately US$114,132,137.10); with the approximate current value of the 5,913 certified claims US$8,521,866,236.75.
The first asset to be expropriated by the Republic of Cuba was an oil refinery in 1960 owned by White Plains, New York-based Texaco, Inc., now a subsidiary of San Ramon, California-based Chevron Corporation (USFCSC: CU-1331/CU-1332/CU-1333 valued at US$56,196,422.73).
The largest certified claim (Cuban Electric Company) valued at US$267,568,413.62 is controlled by Boca Raton, Florida-based Office Depot, Inc. The second-largest certified claim (International Telephone and Telegraph Co, ITT as Trustee, Starwood Hotels & Resorts Worldwide, Inc.) valued at US$181,808,794.14 is controlled by Bethesda, Maryland-based Marriott International; the certified claim also includes land adjacent to the Jose Marti International Airport in Havana, Republic of Cuba. The smallest certified claim is by Sara W. Fishman in the amount of US$1.00 with reference to the Cuban-Venezuelan Oil Voting Trust.
The two (2) largest certified claims total US$449,377,207.76, representing 24% of the total value of the certified claims. Thirty (30) certified claimants hold 56% of the total value of the certified claims. This concentration of value creates an efficient pathway towards a settlement.
Title III of the Cuban Liberty and Democratic Solidarity (Libertad) Act of 1996 requires that an asset had a value of US$50,000.00 when expropriated by the Republic of Cuba without compensation to the original owner. Of the 5,913 certified claims, 913, or 15%, are valued at US$50,000.00 or more. Adjusted for inflation, US$50,000.00 (3.70% per annum) in 1960 has a 2019 value of approximately US$427,267.01. The USFCSC authorized 6% per annum, meaning the 2019 value of US$50,000.00 is approximately US$1,649,384.54.
The ITT Corporation Agreement
In July 1997, then-New York City, New York-based ITT Corporation and then-Amsterdam, the Netherlands-based STET International Netherlands N.V. signed an agreement whereby STET International Netherlands N.V. would pay approximately US$25 million to ITT Corporation for a ten-year right (after which the agreement could be renewed and was renewed) to use assets (telephone facilities and telephone equipment) within the Republic of Cuba upon which ITT Corporation has a certified claim valued at approximately US$130.8 million. ETECSA, which is now wholly-owned by the government of the Republic of Cuba, was a joint venture controlled by the Ministry of Information and Communications of the Republic of Cuba within which Amsterdam, the Netherlands-based Telecom Italia International N.V. (formerly Stet International Netherlands N.V.), a subsidiary of Rome, Italy-based Telecom Italia S.p.A. was a shareholder. Telecom Italia S.p.A., was at one time a subsidiary of Ivrea, Italy-based Olivetti S.p.A. The second-largest certified claim (International Telephone and Telegraph Co, ITT as Trustee, Starwood Hotels & Resorts Worldwide, Inc.) valued at US$181,808,794.14 is controlled by Bethesda, Maryland-based Marriott International.
What Is “Trafficking” According To Libertad Act?
(13) Traffics.--(A) As used in title III, and except as provided in subparagraph (B), a person "traffics" in confiscated property if that person knowingly and intentionally-- (i) sells, transfers, distributes, dispenses, brokers, manages, or otherwise disposes of confiscated property, or purchases, leases, receives, possesses, obtains control of, manages, uses, or otherwise acquires or holds an interest in confiscated property, (ii) engages in a commercial activity using or otherwise benefiting from confiscated property, or (iii) causes, directs, participates in, or profits from, trafficking (as described in clause (i) or (ii)) by another person, or otherwise engages in trafficking (as described in clause (i) or (ii)) through another person, without the authorization of any United States national who holds a claim to the property.
(B) The term "traffics" does not include-- (i) the delivery of international telecommunication signals to Cuba; (ii) the trading or holding of securities publicly traded or held, unless the trading is with or by a person determined by the Secretary of the Treasury to be a specially designated national; (iii) transactions and uses of property incident to lawful travel to Cuba, to the extent that such transactions and uses of property are necessary to the conduct of such travel; or (iv) transactions and uses of property by a person who is both a citizen of Cuba and a resident of Cuba, and who is not an official of the Cuban Government or the ruling political party in Cuba.
“DETERMINATION OF OWNERSHIP OF CLAIMS REFERRED BY DISTRICT COURTS OF THE UNITED STATES
"Sec. 514. Notwithstanding any other provision of this Act and only for purposes of section 302 of the Cuban Liberty and Democratic Solidarity (LIBERTAD) Act of 1996, a United State district court, for fact-finding purposes, may refer to the Commission, and the Commission may determine, questions of the amount and ownership of a claim by a United States national (as defined in section 4 of the Cuban Liberty and Democratic Solidarity (LIBERTAD) Act of 1996), resulting from the confiscation of property by the Government of Cuba described in section 503(a), whether or not the United States national qualified as a national of the United States (as defined in section 502(1)) at the time of the action by the Government of Cuba.”
TITLE III--SEC. 302. LIABILITY FOR TRAFFICKING IN CONFISCATED PROPERTY CLAIMED BY UNITED STATES NATIONALS.
(a) Civil Remedy.-- (1) Liability for trafficking.--(A) Except as otherwise provided in this section, any person that, after the end of the 3-month period beginning on the effective date of this title, traffics in property which was confiscated by the Cuban Government on or after January 1, 1959, shall be liable to any United States national who owns the claim to such property for money damages in an amount equal to the sum of-- (i) the amount which is the greater of-- (I) the amount, if any, certified to the claimant by the Foreign Claims Settlement Commission under the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949, plus interest; (II) the amount determined under section 303(a)(2), plus interest; or (III) the fair market value of that property, calculated as being either the current value of the property, or the value of the property when confiscated plus interest, whichever is greater; and (ii) court costs and reasonable attorneys' fees. (B) Interest under subparagraph (A)(i) shall be at the rate set forth in section 1961 of title 28, United States Code, computed by the court from the date of confiscation of the property involved to the date on which the action is brought under this subsection.
(2) Presumption in favor of the certified claims.--There shall be a presumption that the amount for which a person is liable under clause (i) of paragraph (1)(A) is the amount that is certified as described in subclause (I) of that clause. The presumption shall be rebuttable by clear and convincing evidence that the amount described in subclause (II) or (III) of that clause is the appropriate amount of liability under that clause.
(3) Increased liability.-- (A) Any person that traffics in confiscated property for which liability is incurred under paragraph (1) shall, if a United States national owns a claim with respect to that property which was certified by the Foreign Claims Settlement Commission under title V of the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949, be liable for damages computed in accordance with subparagraph (C).
(B) If the claimant in an action under this subsection (other than a United States national to whom subparagraph (A) applies) provides, after the end of the 3-month period described in paragraph (1) notice to-- (i) a person against whom the action is to be initiated, or (ii) a person who is to be joined as a defendant in the action, at least 30 days before initiating the action or joining such person as a defendant, as the case may be, and that person, after the end of the 30- day period beginning on the date the notice is provided, traffics in the confiscated property that is the subject of the action, then that person shall be liable to that claimant for damages computed in accordance with subparagraph (C).
(C) Damages for which a person is liable under subparagraph (A) or subparagraph (B) are money damages in an amount equal to the sum of-- (i) the amount determined under paragraph (1)(A)(ii), and (ii) 3 times the amount determined applicable under paragraph (1)(A)(i). (D) Notice to a person under subparagraph (B)-- (i) shall be in writing; (ii) shall be posted by certified mail or personally delivered to the person; and (iii) shall contain-- (I) a statement of intention to commence the action under this section or to join the person as a defendant (as the case may be), together with the reasons therefor; (II) a demand that the unlawful trafficking in the claimant's property cease immediately; and (III) a copy of the summary statement published under paragraph (8). (4) Applicability.--(A) Except as otherwise provided in this paragraph, actions may be brought under paragraph (1) with respect to property confiscated before, on, or after the date of the enactment of this Act.
(B) In the case of property confiscated before the date of the enactment of this Act, a United States national may not bring an action under this section on a claim to the confiscated property unless such national acquires ownership of the claim before such date of enactment. (C) In the case of property confiscated on or after the date of the enactment of this Act, a United States national who, after the property is confiscated, acquires ownership of a claim to the property by assignment for value, may not bring an action on the claim under this section.
(5) Treatment of certain actions.--(A) In the case of a United States national who was eligible to file a claim with the Foreign Claims Settlement Commission under title V of the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949 but did not so file the claim, that United States national may not bring an action on that claim under this section. (B) In the case of any action brought under this section by a United States national whose underlying claim in the action was timely filed with the Foreign Claims Settlement Commission under title V of the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949 but was denied by the Commission, the court shall accept the findings of the Commission on the claim as conclusive in the action under this section.
(C) A United States national, other than a United States national bringing an action under this section on a claim certified under title V of the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949, may not bring an action on a claim under this section before the end of the 2-year period beginning on the date of the enactment of this Act.
(D) An interest in property for which a United States national has a claim certified under title V of the International Claims Settlement Act of 1949 may not be the subject of a claim in an action under this section by any other person. Any person bringing an action under this section whose claim has not been so certified shall have the burden of establishing for the court that the interest in property that is the subject of the claim is not the subject of a claim so certified. (6) Inapplicability of act of state doctrine. No court of the United States shall decline, based upon the act of state doctrine, to make a determination on the merits in an action brought under paragraph (1).
(7) Licenses not required. (A) Notwithstanding any other provision of law, an action under this section may be brought and may be settled, and a judgment rendered in such action may be enforced, without obtaining any license or other permission from any agency of the United States, except that this paragraph shall not apply to the execution of a judgment against, or the settlement of actions involving, property blocked under the authorities of section 5(b) of the Trading with the Enemy Act that were being exercised on July 1, 1977, as a result of a national emergency declared by the President before such date, and are being exercised on the date of the enactment of this Act.
LINK To Complete Analysis